INTRODUCTION
Nearly 20% of patients (pts) are ≥ 80 years (yrs) of age at the time of CLL diagnosis. Increased medical comorbidities, as well as declining functional status and organ function, often accompany advanced age. However, clinical trials often enroll a disproportionally low number of people from this age demographic due to stringent eligibility parameters, which provides limited evidence to guide decisions. Here, we report clinical characteristics and outcomes of pts ≥ 80 yrs of age at the time of CLL diagnosis.
METHODS
Between 1/1995 and 3/2020, we identified previously untreated CLL pts from the Mayo Clinic CLL Database who were ≥ 80 yrs of age at the time of CLL diagnosis, and seen within 3 yrs of diagnosis. Baseline characteristics, treatments administered, and time to first treatment (TFT) were analyzed for all pts. Overall survival (OS) was measured from diagnosis date in all pts and separately from treatment date for treated pts. Time to next treatment (TTNT) was measured in treated pts from first treatment date to date of second treatment or last known treatment. TFT and TTNT were analyzed accounting for competing risk of death. Standardized mortality ratio (SMR) compared observed survival to survival in a Minnesota population. Cox multivariable regression models were used to determine which factors were associated with OS (treatment as a time-dependent covariate) and TTNT (accounting for competing risk of death).
RESULTS
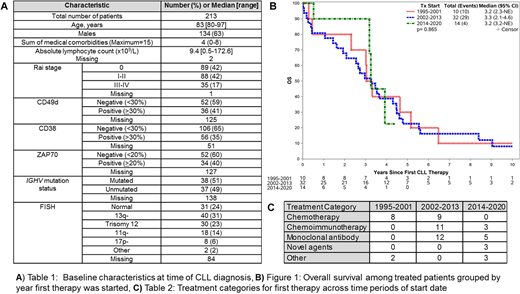
Among the 213 pts identified, the median age was 83 yrs (range 80-97); baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The median number of medical comorbidities among all pts was 4 (range 0-8). At least 1 comorbidity was present in 97% of pts, most commonly hypertension (57%), genitourinary (n=48%), rheumatological (46%), and dyslipidemia (n=43%).
Median follow-up was 3.8 yrs. A total of 56 pts received treatment and the median TFT was 6.7 yrs. Over this 25 year interval, the treatment approaches included monoclonal antibody alone (n=17), chemotherapy alone (n=17), or chemoimmunotherapy (n=14), novel agents (n=3), and multi-agent Richter's transformation regimens (n=5). Chlorambucil-based treatments (chlorambucil n=13, chlorambucil, prednisone n=3) were the most frequently used chemotherapy regimens. The most common chemoimmunotherapy regimens included rituximab, cyclophosphamide, prednisone (RCP) with (n=3) or without vincristine (n=6), and chlorambucil with an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (n=4; obinutuzumab n=2, rituximab n=2). Among 17 pts who received monoclonal antibody alone, treatments included rituximab alone (n=11), rituximab plus methylprednisolone (n=2), obinutuzumab (n=2), and rituximab with alemtuzumab (n=2). Frontline novel agent treatments included ibrutinib alone (n=1), acalabrutinib alone (n=1), and ibrutinib, obinutuzumab, venetoclax (n=1). Five pts with Richter's transformation (diagnosed concurrent with CLL n=4) received multi-agent chemotherapy. Among the 56 treated pts, 22 pts received second line therapy after a median TTNT of 2.8 yrs from start of first therapy. The most common second line treatments were chlorambucil-based (n=6) and rituximab-based (n=6) regimens. Age, sex, absolute lymphocyte count, del17p, and unmutated IGHV were not predictive of TTNT.
The median OS among all 213 pts was 4.6 yrs. SMR was 1.2 (p=0.008) when excluding pts with Richter's transformation. In univariable analyses, receipt of therapy (HR 3.92, 95%CI 2.11-7.28; p<0.001), age (per 5 year increase; HR 1.84, 95%CI 1.43-2.38; p<0.001) and unmutated IGHV (HR 2.03, 95%CI 1.12-3.67; p=0.02) were predictors of shorter OS. The OS among pts who received treatment (Figure 1) was similar when compared across time periods of treatment start year grouped as 1995-2001 (n=10), 2002-2013 (n=32), and 2014-2020 (n=14). Treatment categories by time period are shown in Table 2.
CONCLUSIONS
In this study of 213 pts ≥ 80 yrs of age at time of CLL diagnosis, the median time to first therapy was ~7 yrs. Although survival outcomes did not differ by era across the 25-year span of this study, pts treated with novel agents were underrepresented and are a patient population which warrants additional evaluation. The finding that pts with CLL in this cohort had a 20% higher risk of death compared to an age- and sex-matched population emphasize the need for ongoing efforts to improve clinical outcomes for CLL pts in this demographic category.
Kenderian:Torque: Consultancy; Mettaforge: Patents & Royalties; Humanigen: Consultancy, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Novartis: Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Tolero: Research Funding; Sunesis: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Lentigen: Research Funding. Wang:Incyte: Research Funding; Innocare: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Shanafelt:Genentech, Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company, AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline, and Merck: Research Funding; Mayo Clinic: Patents & Royalties: and other intellectual property. Braggio:DASA: Consultancy; Bayer: Other: Stock Owner; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding. Kay:Morpho-sys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyer Squib: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Oncotracker: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Juno Theraputics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Rigel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Cytomx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sunesis: Research Funding; MEI Pharma: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Acerta Pharma: Research Funding; Dava Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ding:alexion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Abbvie: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Beigene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; DTRM: Research Funding; Merck: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Parikh:Merck: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Ascentage Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria; Verastem Oncology: Honoraria; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.